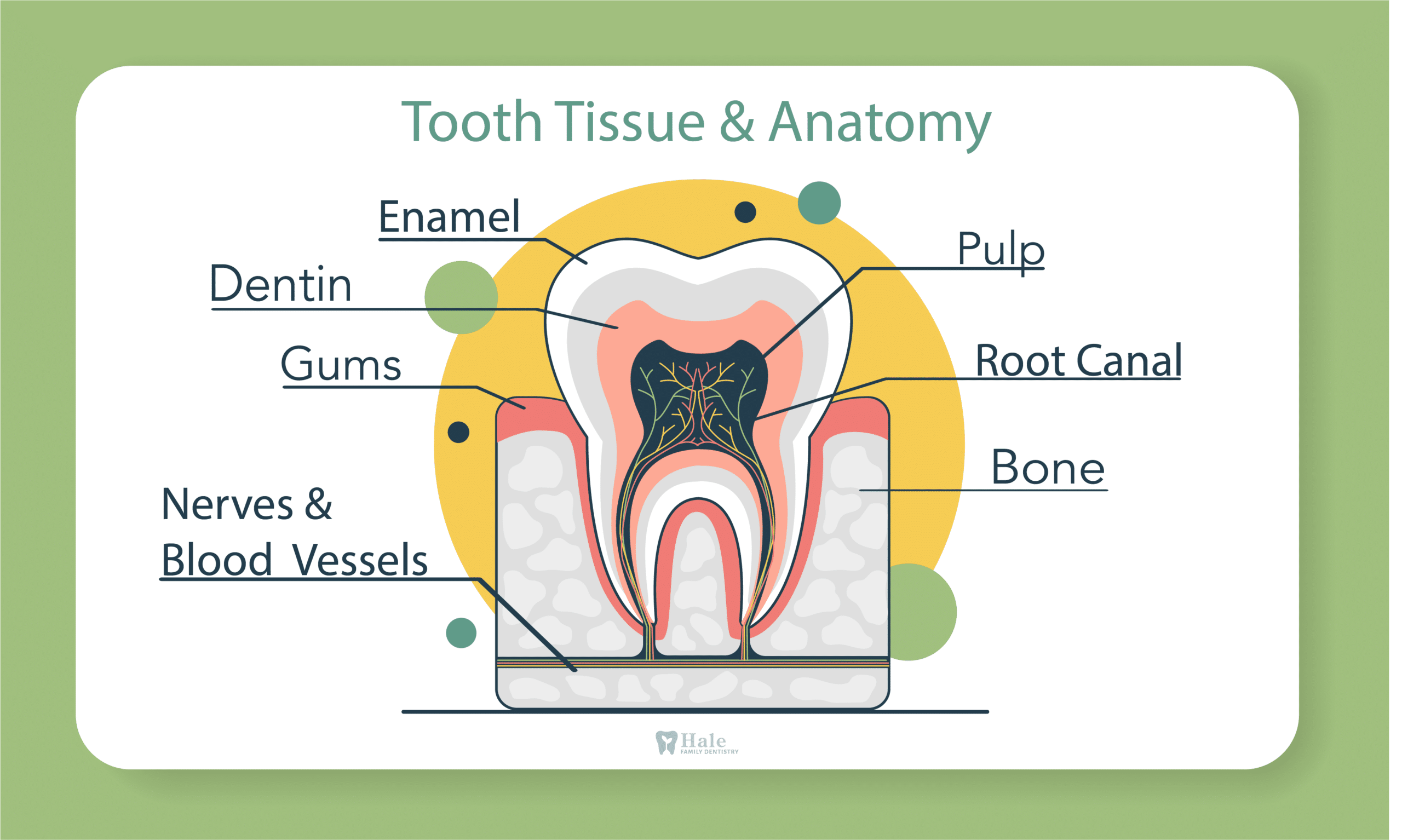
What is Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay, often referred to as cavities or dental caries, is an oral health concern affecting both baby teeth and permanent teeth in millions worldwide. It’s a dental disease that begins when harmful acids in your mouth start to erode the protective outer layer, or tooth surface, of your teeth.
The Causes of Dental Decay
The main culprits behind tooth decay are bacteria that reside in our mouths. These bacteria transform leftover sugars from our meals into harmful acids, producing dental plaque in the process. Over time, these acids attack the tooth enamel, leading to decay.
Tooth decay is typically diagnosed during a regular dental check-up. Your dentist will examine your teeth, looking for any visible signs of decay, such as holes or staining. They may also ask about any symptoms you’ve been experiencing, like tooth pain or sensitivity.
Who is most vulnerable?
- Children and teenagers: Despite their boundless energy and bright smiles, kids are the some of the most prone to decay and cavities. Why so? A fondness for sugary delights and sometimes, a not-so-perfect brushing routine. But don’t worry, with a bit of guidance and healthier habits, they can keep tooth decay at bay!
- Older adults: As we age, gums might recede, leaving roots more exposed to decay. Years of wear and tear can also mean more fillings, which can become new hiding spots for cavities over time.
- People with dry mouth: Often due to certain medications or medical treatments, Less saliva means less natural washing away of food particles and neutralizing of harmful acids, making teeth more prone to decay.
- People with certain medical conditions: Cancer patients under radiation, diabetics, or conditions such as Sjögren’s syndrome, are more susceptible to tooth decay.
- People with diabetes: People with diabetes are more susceptible to certain oral health issues due to their higher susceptibility to infections, including gum disease, which can subsequently lead to tooth decay.
But here’s the good news: no matter type of person, tooth decay isn’t inevitable.
Signs and Symptoms of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay often begins silently, with no initial discomfort. However, as it progresses through the stages of tooth decay symptoms such as toothache, tooth sensitivity, pain when eating cold or sweet food, visible holes in your teeth, black spots (in late stages), or white spots (in early stages) may appear.
The symptoms of dental caries (tooth decay) may vary depending on the extent and location of the decay. Here are some of the top symptoms:
- Toothache or Tooth Pain: This is often the most noticeable sign of dental caries. The pain can be sharp, spontaneous, or it may be a dull ache that comes and goes.
- Tooth Sensitivity: This is often experienced when eating or drinking something hot, cold, or sweet. The sensitivity is usually the result of enamel erosion which exposes the more sensitive layers of the tooth.
- Visible Holes or Pits in Teeth: In advanced stages of decay, visible holes or pits may appear in the affected teeth.
- Brown, Black, or White Staining on Tooth Surface: These are often signs of enamel demineralization and decay.
- Pain When Biting Down: This can occur when the decay has reached the dentin layer of the tooth, or the tooth root, causing discomfort or pain when biting or chewing.
- Bad Breath or Unpleasant Taste: Decay and bacteria can cause persistent bad breath or an unpleasant taste in your mouth.
- Swelling in the Gum Near a Tooth: This could indicate an abscess resulting from advanced tooth decay.
It’s important to note that the earliest stages of tooth decay might not present any symptoms at all. That’s why regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s a good idea to schedule a visit to your dentist as soon as possible.
X-rays and other Tests for Assessments
Dentists use a combination of visual inspection and professional tools such as X-Rays to view deeper layers of the tooth. They’ll look for any changes in the color or texture of your teeth, including white spots which can be an early sign of decay.
In addition to visual examination, dentists use X-rays to detect cavities between teeth and under fillings. X-rays can also show the extent of decay, including whether it has affected the tooth’s pulp (the inner part of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels).
Did you know? Only 40% of a tooth is seen with the naked eye, which is why x-rays are a crucial part of a dental exam.
Filling Treatments for Tooth Decay
The treatment for tooth decay depends on its severity. Early-stage decay, often signaled by white spots on the tooth surface, can be reversed with fluoride treatments and a reduced sugar intake. More advanced cases, like a tooth abscess, may require more in-depth care and dentist analysis. Untreated dental decay can quickly lead to a sore mouth, infection, or sometimes tooth loss.
Dental Procedures for Treating Cavities
Fillings are the most common treatment for cavities. The decay is removed, and the area is filled with materials like silver, gold, porcelain, or a composite resin. Crowns are used when the decay is extensive, and the tooth structure needs to be restored.
In extreme cases where the decay has reached the tooth’s pulp, a root canal treatment may be necessary. This involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning and shaping the inside of the root canal, then filling and sealing the space.
If the tooth is too far gone, and a root canal is no longer a good treatment option, an extraction will be recommended. The good news about this is that modern dentistry has come a long way and dental prosthetics like implants, bridges, or dentures can be used to restore appearance and function similar to natural teeth.
Dental Sealants for Kids and Adults
Dental sealants can be used on both children and adults but are mostly seen in pediatric dental settings. Sealants are used as a preventive dental treatment that helps to decrease the likelihood of developing deep dental caries in the deep grooves of the teeth.
These grooves, also known as pits and fissures, are common sites for bacteria to accumulate, making them vulnerable to tooth decay.
Dental sealants are a thin, protective coating that is applied to the chewing surfaces of the molars and premolars, creating a barrier that prevents food particles and bacteria from settling in the deep grooves of the teeth.
Prevention Tips and Overall Health
Consuming a Balanced Diet Low in Sugar and Starchy Foods
A diet limiting sugary snacks and starchy foods helps prevent tooth decay. These foods can stick to your teeth and promote bacterial growth. Instead, focus on fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. We’ve compiled a list of these sticky, starchy foods that you may not even know are potential risks for tooth decay.
- Bread, especially white bread: The simple carbohydrates in bread can quickly break down into sugar in your mouth.
- Potato Chips: These snacks can easily get stuck in and between your teeth.
- Pasta: Like bread, the simple carbs in pasta can quickly break down into sugar.
- Rice: Its sticky nature means it can easily adhere to the tooth surface.
- Crackers: These can stick to the teeth, and the starches convert to sugar which can lead to tooth decay.
- Cereal: Some cereals can be sticky and adhere to teeth, especially those that are high in sugar.
Limiting Sugary Drinks and Snacks During the Day
- Limiting the intake of sugary drinks and snacks during the day is another effective strategy. When you consume these items, bacteria in your mouth produce acids that can erode tooth enamel.
Drink More Water
- Especially after consuming sugary food and drinks! This can help wash free the food debris between your teeth and help prevent further decay.
Brushing Twice a Day with Fluoride Toothpaste
- Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste removes plaque and reduces the risk of tooth decay. Fluoride helps strengthen tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay.
Tips to Avoid Cavities
Preventing tooth decay involves a combination of good oral hygiene, a balanced meal, and regular dental cleanings. Keeping your teeth clean by brushing and flossing to remove dental plaque, and reducing the intake of sweet food and drinks, limits the fuel for harmful bacteria. Additionally, don’t skip your dental checkups! Your dentist can catch the early stages of tooth decay, making treatment easier, more comfortable, and less time consuming in the long run.
Remember, a proactive approach to oral hygiene, including attention to any symptoms like tooth sensitivity, dry mouth, or bad breath, and regular visits to your dentist are the best ways to prevent cavities and maintain a healthy smile.
If you think you may have a cavities or looking for answers regarding a tooth, give our office a call today!
[publishpress_authors_box layout=”boxed” show_title=”true”]